j2eDX
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 05:36 AM |

|
|
Torsion Bar, how does it work?
I'm in the process of putting ideas together for a 3 wheeler project. The hardest part is probably desigining the suspension work into the
chassis. I am planning to use the f1 suspension layout with torsion bar, but I am still not sure if the way i know it works is correct. So I have
included a picture depicting how I think it works. I would like to hear your inputs.
*I made a mistake on the picture. The arrow of the rod on side 2 should be going down, not up*
[Edited on 16/3/07 by j2eDX]
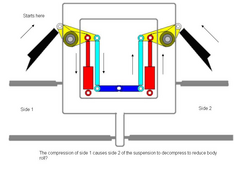 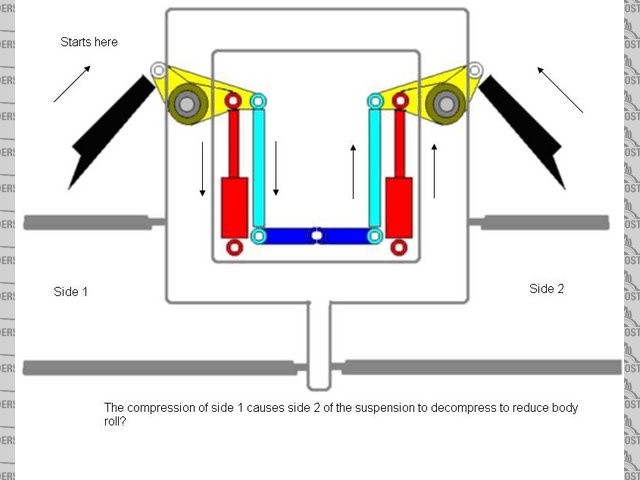
Rescued attachment pushrod2.JPG
|
|
|
|
|
designer
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 06:57 AM |

|
|
This set up is very elaborate for a three wheel project.
The important thing is to keep things simple.
Pushrods and torsion bars are fine for F1 and other hi-tech machines for the precise wheel control they provide.
For the road use springs and if you want to go for lucks, use rockers.
This uses a lot less parts and is easier to build.
|
|
|
Kissy
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 06:58 AM |

|
|
Torsion Bar, is exactly as it says: effectively an uncoiled spring; or to look at it correctly from an historic point of view, a coil spring is a
compact torsion bar. Basically a length of spring steel or other suitably elastic material is anchored at one end (typ. to the chassis). The other
end is restrained to allow it to rotate, with a lever at a right-angle to the axis of the bar. The downside for most would-be users is the
availability of a choice of bars which are the equivalent of different rate coil springs. They were famously used on the front end of morris Minors
and more infamously Marinas. IIRC they were used on Porsche 944s. They do however have the advantage of being compact in certain installations.
HTH.
|
|
|
Macbeast
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 07:38 AM |

|
|
What happens if both wheels on your drawing meet the same obstacle, like a speed bump ?
|
|
|
britishtrident
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 07:41 AM |

|
|
I think you mean an anti-roll bar (ARB) or perhaps a Z bar as used on Formula Vee racers.. A Z bar is the opposite of an ARB it is used to decrease
roll stiffness
Although both ARB and Z bar is a torsion bar, in automotive suspension use the term torsion is normally reserved for whee the torsion bar is the main
suspension spring, such as on the Morris 1000, Marina, 1950/60s Daimler, Chrysler Alpine, Chrysler Horizon, Rover 213 and Lotus 72.
Anti-roll bars and other torsion bars calculations are based on simple torsion theory, but it can be tricky to get the required rate without over
stressing the material at the outer surface of the bar.
The Fred Phun book "How to Make Your Car Handle" has simple formula for calculating torsion bar stiffness.
However in 3 wheeler all the roll stiffness comes from one end, using an anti-roll bar will increase wheel lifting. Using a Z bar will decrease wheel
lifting but cause excessive roll.
[Edited on 16/3/07 by britishtrident]
|
|
|
Mal
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 07:48 AM |

|
|
Torsion bar suspension
The Hudson Kindred Spirit 3 wheeler has front torsion bar suspension taken from the Renault 5.
One thing to bear in mind with torsion bars is that they require a stiff mounting bracket at the chassis end to take the torque reaction of the wheel
input loads.
Also, it is difficult to alter the spring rate, whereas coil spring are readily changeable.
Mal.
|
|
|
Mr Whippy
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 08:09 AM |

|
|
quote:
Originally posted by Macbeast
What happens if both wheels on your drawing meet the same obstacle, like a speed bump ?
like above your going to be introuble there. Sorry not a correct use of the torsion bar system, use seperate bars or coilovers with an anti-roll bar
to control body roll.
Fame is when your old car is plastered all over the internet
|
|
|
Bob C
|
| posted on 16/3/07 at 01:03 PM |

|
|
Move the uproght link from the cross bar to outside the rocker pivot on one side
voila
Bob
|
|
|
C10CoryM
|
| posted on 17/3/07 at 02:57 AM |

|
|
The light blue and dark blue links are the roll control. The grey in the middle of the yellow rocker is the torsion bar.
Way these work is in roll the blue links twist giving roll stiffness. In 2 wheel bump the pivot in the dark blue link moves down in this case and
compresses a seperate coilover. This is the bump control.
The whole idea is to un-couple the bump and roll forces.
Here is a picture of it for real to clear things up.
http://www.gurneyflap.com/Resources/renaultsus.jpg
Pretty isn't it? 
Cheers.
"Our watchword evermore shall be: The Maple Leaf Forever!"
|
|
|









